Gum Grafts
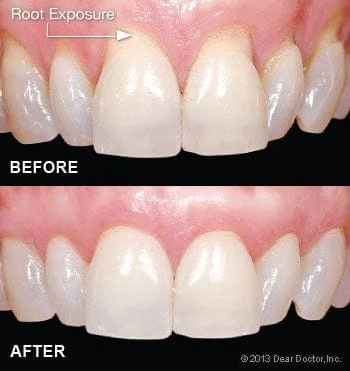
Inside your mouth, gum tissue forms a barrier that resists the vigorous mechanical (and microbial) effects of eating, chewing and biting. When the tooth's roots lose the protection of healthy gum tissue, they can become extremely sensitive to hot or cold temperatures, causing pain when you consume many foods and drinks. Worse, missing gum tissue makes it easier for bacteria to penetrate the roots and cause decay — or for minor trauma to result in rapid gum recession. In either case, the eventual result may be tooth loss. That's why proper treatment of gum recession is so important.
Treating Gum Recession With Gingival Grafting
After a thorough examination and assessment of your teeth, gums and overall health, the gingival grafting procedure may be recommended. The tissue used in this procedure may be obtained from a variety of sources: an area next to the area of recession, from the hard palate, or donated tissue from another person, which has been medically processed to make it safe to use.
There are several different methods of grafting. For example, if you have lost gum tissue in an area of your mouth that's not highly visible when you talk or smile, additional gum tissue can be placed there to prevent further recession without trying to cover the tooth-root surface completely. This procedure is referred to as a free gingival graft (since the tissue is separated from its blood supply), and it takes about 45 minutes to perform. It is very predictable with a very high success rate. If the objective is to cover root surfaces, the procedure becomes more complicated and will take longer, but is still very successful.
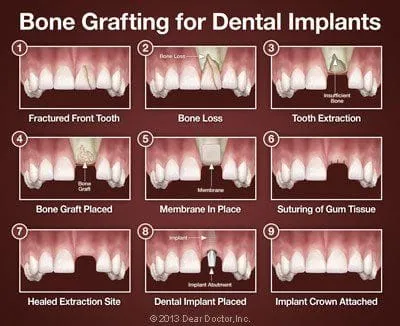
Bone Grafts
Bone grafting, normally a minor surgical procedure done in the dental office, is used to build up new bone in the area of your jaw that used to hold teeth. A small incision is made in your gum to expose the bone beneath it, and then grafting material is added. Most often, the grafting material is processed bone that serves as a scaffold, around which your body will actually deposit new bone cells. The grafting material will eventually be absorbed by your body and replaced by your own new bone.
The grafting material needed can come from a variety of sources. Sometimes it comes from your own body. Very often, however, it is bone from an animal or human donor that is processed by a laboratory to make it sterile and safe. Grafting material can even be synthetic. It comes in a variety of forms: powder, granules, putty or even a gel that can be injected through a syringe.